Temperature Control: Air-cooled Chiller Vs. Water-cooled Chiller
2024-07-18 Page view:
In industrial settings, temperature control is crucial particularly for plastic processing applications. Two common types of cooling equipment used for temperature control are air-cooled and water-cooled chillers. Each chiller type has unique characteristics and advantages, making them suitable for different scenarios. Let’s explore the similarities and differences between the two types of industrial chillers.

Working Principles and Structure
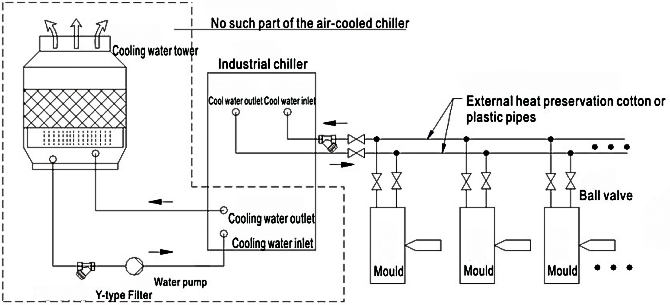
Air-cooled chillers mainly rely on the surrounding air and the air generated by fans to cool the refrigerant in the condenser, thereby dissipating heat into the atmosphere. The chiller is mainly composed of compressor, condenser, evaporator, and fan. Air-cooled chillers are typically easier to install and maintain, as they do not require a cooling tower.

The water-cooled chiller uses water as the cooling medium to transfer heat to the cooling water, and then dissipates the heat to the atmosphere through a cooling tower. The water-cooled chiller is mainly composed of components such as compressor, condenser, evaporator, and water pump. The structure is relatively more complex but it provides stronger adaptability to environmental temperature.
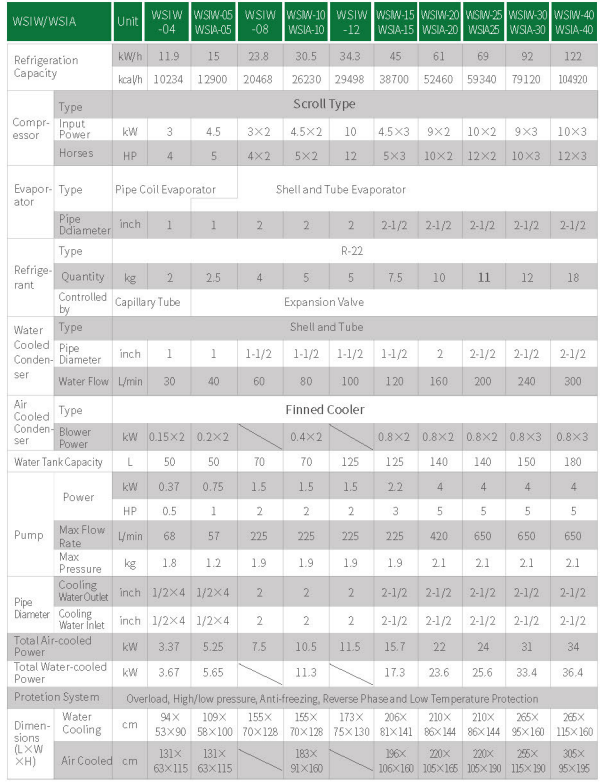
Performance and Efficiency
During the operation of air-cooled chillers, they are greatly affected by the ambient temperature. When the ambient temperature is high, the refrigeration efficiency decreases while the noise and energy consumption increase. However, air-cooled chillers do not require any additional cooling water system, making them advantageous in areas with limited access to water resources or restrictions for water consumption.
Water-cooled chillers have high refrigeration efficiency and stability especially in high-temperature environments. Meanwhile, water-cooled chillers typically use high-efficiency compressors and condensers, which further improve their energy efficiency ratio.
Cost
The initial investment of air-cooled chiller is relatively more cost-effective because of their simple structure and no need for additional cooling water systems. However, running an air-cooled chiller requires more energy consumption to maintain stable cooling performance in high-temperature environments, thereby increasing operating costs.
The initial investment of water-cooled chillers is relatively higher but they have a lower operating costs in the long-term. Due to its ability to maintain high refrigeration efficiency in high-temperature environments, water-cooled chillers can save a significant amount of energy costs. In addition, water-cooled chillers typically have a longer service life and lower failure rates, which also reduces maintenance and replacement costs.
Temperature Control Applications
Air-cooled chillers may have high noise levels as the fan generates noise during operation. Therefore, air-cooled chillers are suitable for places with low ambient temperatures, limited space, or low noise requirements.
Water-cooled chillers require more space and have certain requirements for water quality as the cooling water circulation may be affected by water quality. Thanks to its high refrigeration efficiency and stability, it is well-suited for locations that demand superior cooling performance and consistent reliability.
Industrial Chiller Supplier
Both air-cooled and water-cooled chillers have their own unique features. In order to select the most suitable chiller model for your operation, it depends on the factors of specific application environment, cooling requirements, installation conditions, and budget. If you are looking for a temperature control unit for your plastic processing production, feel free to contact us. Our sales team will comprehensively consider your actual needs and environmental conditions to choose the most ideal cooling solution for you.



